Understanding the Arabic Letters: Ba, Ta, and Tha
The Arabic alphabet can seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of each letter’s forms, it becomes much simpler. This guide focuses on three important letters: Ba (ب), Ta (ت), and Tha (ث). We’ll explore how these letters change shape depending on their position in a word: initial, medial, and final.
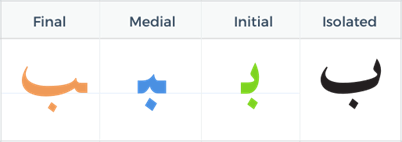
The Arabic Letter Ba (ب)
Ba (ب) is equivalent to the English “B” sound. It has one dot below the main letter body.
Forms of Ba
- Initial: بـ (at the beginning of a word)
- Example: باب (bab) – door
- Example: باب (bab) – door
- Medial: ـبـ (in the middle of a word)
- Example: نبات (nabat) – plant
- Example: نبات (nabat) – plant
- Final: ـب (at the end of a word)
- Example: كتاب (kitab) – book
- Example: كتاب (kitab) – book
- Isolated: ب (when the letter stands alone)
- Example: بَيت (bayt) – house
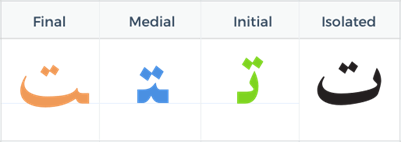
The Arabic Letter Ta (ت)
Ta (ت) is equivalent to the English “T” sound. It has two dots above the main letter body.
Forms of Ta
- Initial: تـ (at the beginning of a word)
- Example: تاج (taj) – crown
- Example: تاج (taj) – crown
- Medial: ـتـ (in the middle of a word)
- Example: متجر (matjar) – shop
- Example: متجر (matjar) – shop
- Final: ـت (at the end of a word)
- Example: بيت (bayt) – hous
- Example: بيت (bayt) – hous
- Isolated: ت (by itself)
- Example: توت (tūt) – berry
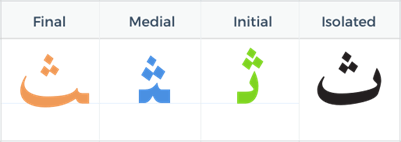
The Arabic Letter Tha (ث)
Tha (ث) is similar to the “Th” sound in “thin”. It has three dots above the main letter body.
Forms of Tha
- Isolated: ث (by itself)
- Example: ثلاث (thalāth) – three
- Example: ثلاث (thalāth) – three
- Initial: ثـ (at the beginning of a word)
- Example: ثمن (thaman) – price
- Example: ثمن (thaman) – price
- Medial: ـثـ (in the middle of a word)
- Example: كمثرى (kummathrā) – pear
- Example: كمثرى (kummathrā) – pear
- Final: ـث (at the end of a word)
- Example: بحث (baḥth) – research
Ready to dive deeper into the beautiful world of the Arabic language? Download Kaleela today and unlock a fun and effective way to learn Arabic!



